Preventive Maintenance Schedule for Conveyor Systems at a Bulk Material Handling Facility
1. Purpose and Scope
- This preventive maintenance schedule is designed to ensure safe, reliable, and efficient operation of belt conveyor systems used for bulk material handling. It applies to all conveyors, including feed conveyors, transfer conveyors, stacking conveyors, and reclaim systems. The schedule addresses mechanical, electrical, and structural components and emphasizes safety, uptime, and equipment longevity.

2. Safety Requirements (Applies to All PM Tasks)
• Follow lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures before performing maintenance.
• Verify zero energy state (electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic).
• Wear required PPE: hard hat, safety glasses, gloves, steel-toe boots, and fall protection where required.
• Ensure conveyor is clean and free of residual material that could shift or fall.
• Never work on a moving conveyor.

3. Daily Inspections (Operator or Maintenance Rounds)
Performed at the start of each shift or daily during operation.
• Inspect belt tracking and alignment; note any edge rubbing or wandering.
• Listen for unusual noises from idlers, pulleys, gearboxes, or motors.
• Check for visible belt damage: tears, fraying, missing fasteners, or splice separation.
• Verify guards, emergency pull cords, and safety switches are in place and functional.
• Observe material flow at loading and transfer points for spillage or buildup.
• Check take-up systems for proper tension and travel.
• Look for oil leaks, grease leaks, or overheated components.
• Record findings in the maintenance log.
 4. Weekly Preventive Maintenance
4. Weekly Preventive Maintenance
Performed by maintenance technicians.
• Clean spilled material from under and around conveyors.
• Inspect idlers and rollers for seizure, excessive vibration, or wear; tag failed units for replacement.
• Check belt cleaners and scrapers; adjust tension and replace worn blades as needed.
• Inspect pulley lagging for wear, glazing, or separation.
• Check fasteners, brackets, and supports for looseness or damage; tighten as required.
• Test emergency stops and pull-cord switches for proper function.
• Inspect electrical conduits, junction boxes, and cable trays for damage or dust intrusion.

5. Monthly Preventive Maintenance
Performed during planned downtime where possible.
• Lubricate bearings, take-ups, and other grease points per OEM recommendations.
• Inspect drive assemblies: motor, gearbox, couplings, and backstops for wear, alignment, and vibration.
• Measure belt speed and verify against design values.
• Inspect belt splices (mechanical or vulcanized) for wear, cracking, or separation.
• Check chute liners, skirting rubber, and impact beds; replace worn components.
• Inspect structural steel, walkways, handrails, and platforms for cracks, corrosion, or deformation.
• Verify conveyor take-up travel and adjust if nearing limits.
 6. Quarterly Preventive Maintenance
6. Quarterly Preventive Maintenance
More detailed inspections and condition monitoring.
• Perform vibration analysis on motors, gearboxes, and major pulleys.
• Conduct thermal imaging of electrical panels, motors, and bearings.
• Inspect and align drive pulleys, bend pulleys, and tail pulleys.
• Check belt thickness and wear patterns at critical locations.
• Inspect and test belt misalignment switches, speed switches, and zero-speed sensors.
• Verify braking systems and backstops function properly under load.
• Review maintenance records and failure trends to identify recurring issues.
7. Semi-Annual Preventive Maintenance
Performed during extended shutdowns if possible.
• Drain and replace gearbox oil per manufacturer specifications; sample oil for analysis.
• Inspect and service hydraulic or gravity take-up systems.
• Perform detailed inspection of loading zones, including impact idlers and support frames.
• Check conveyor frames for alignment over long runs; correct sag or misalignment.
• Inspect electrical motor control centers (MCCs) and variable frequency drives
(VFDs) for dust buildup, loose connections, and cooling performance.
• Replace worn idlers proactively in high-load or high-wear areas.
 8. Annual Preventive Maintenance
8. Annual Preventive Maintenance
Major inspection and overhaul activities.
• Conduct a full belt condition assessment to determine remaining service life.
• Inspect and refurbish or replace major pulleys as required.
• Verify conveyor capacity, power draw, and operating efficiency against original design.
• Inspect foundations, anchor bolts, and structural supports for settlement or corrosion.
• Review safety systems and update risk assessments.
• Update PM procedures based on lessons learned, equipment upgrades, and OEM recommendations.
9. Documentation and Continuous Improvement
• All PM activities must be documented in the computerized maintenance management system (CMMS).
• Track downtime, failures, and corrective maintenance to improve PM intervals.
• Use condition-based monitoring data to transition from time-based to predictive maintenance where feasible.
• Train operators and maintenance personnel regularly on conveyor operation, inspection, and safety.
10. Conclusion
A disciplined preventive maintenance program is essential for reliable conveyor operation in a bulk material handling facility. By following this schedule, the facility can reduce unplanned downtime, extend equipment life, improve safety, and lower total maintenance costs while ensuring consistent material flow and operational efficiency.










 SGCO® Enhances Chute Performance and Longevity
SGCO® Enhances Chute Performance and Longevity 







 4. Weekly Preventive Maintenance
4. Weekly Preventive Maintenance
 6. Quarterly Preventive Maintenance
6. Quarterly Preventive Maintenance
 8. Annual Preventive Maintenance
8. Annual Preventive Maintenance


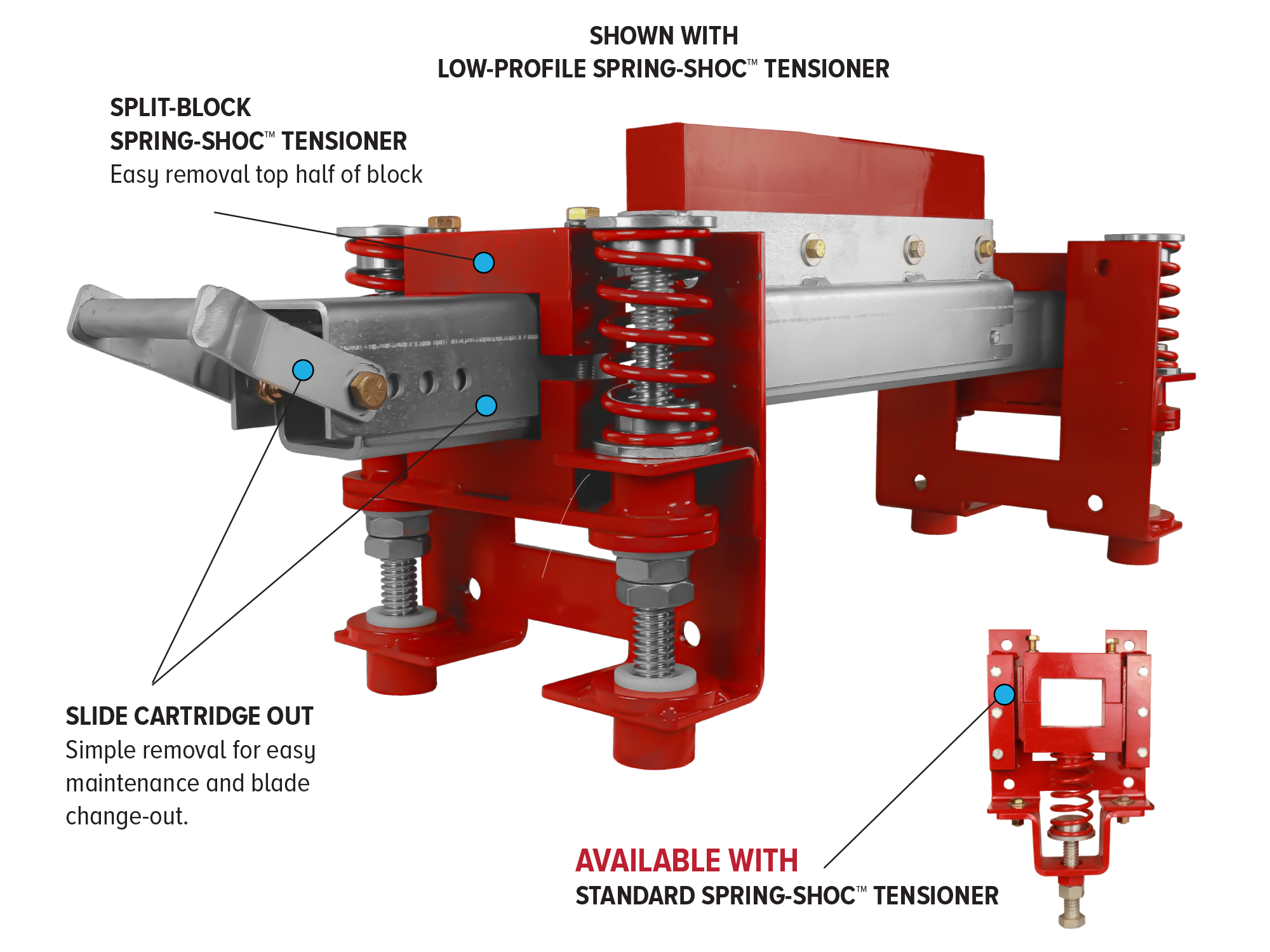
 Why It Matters: Operational Gains and ROI
Why It Matters: Operational Gains and ROI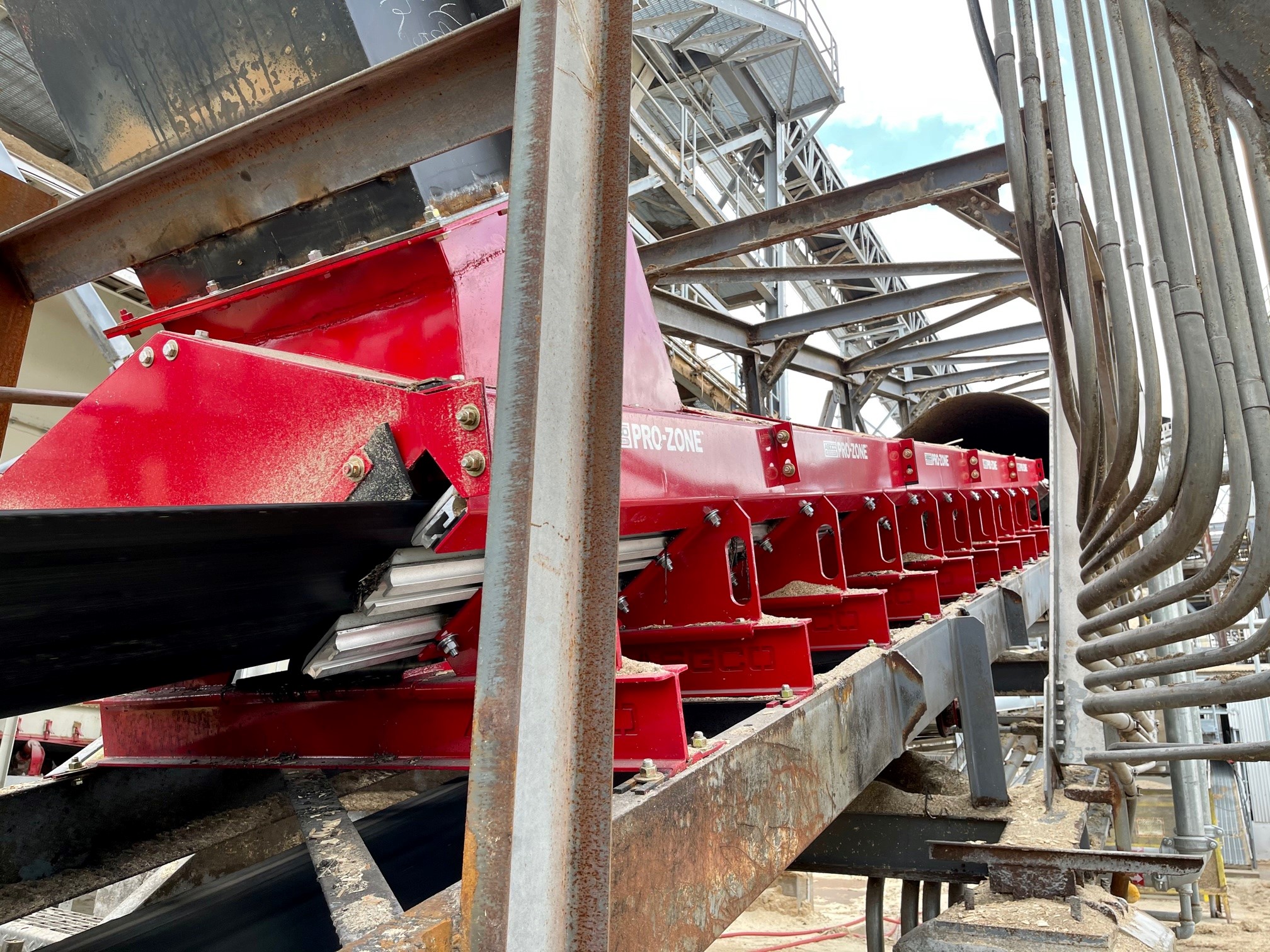

 Product Quality: Dust contamination can compromise the quality of the bulk materials being handled. In industries like bio-fuels (pellets), limestone, coal and other commodities where maintaining product size is critical. Containing dust ensures that the final product meets quality standards.
Product Quality: Dust contamination can compromise the quality of the bulk materials being handled. In industries like bio-fuels (pellets), limestone, coal and other commodities where maintaining product size is critical. Containing dust ensures that the final product meets quality standards.


 Preventing Belt Damage and Wear:
Preventing Belt Damage and Wear:











 loading...
loading...